Category: Science People
-
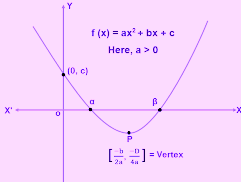
Quadratic Equations 2
Quadratic equations is any equation of the form ax2+bx+c=0 where a is not zero. In other words, quadratic equation is a quadratic expression that is equated to a zero as a value. solving quadratic equations methods of solving quadratic equations includes: solving Quadratic Equations by factorization consider the quadratic equation: x2+3x-54 = 0. we find…
-
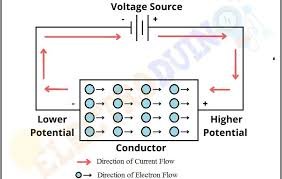
Potential Difference: Powerful Impact on Electrical Systems
The potential difference between to points A and B (Vab) of a conductor is defined as the work done in moving unit charge from point B to A of the conductor. The figure below illustrates the movement of charge in a conductor under the influence of a potential difference. One volt is equal to one…
-

The ohm’s law
Georg Simon Ohm In 1825, Georg Ohm tested wires of varying length, diameter, and material to complete a circuit. He found that his data for current, voltage and resistance could be modeled through a special equation, which we know today as Ohm’s Law. The Ohm’s law summaries about the relation that exists between the voltage…
-

8 IMPORTANT TERMS IN EDUCATION RESEARCH
Basic terms in education research represents the vocabulary used in the topic. In educational research, there are several key terms and concepts that are commonly used. Here are some of the basic ones: Population It refers to the group of individual, events/ objects having common observable characteristics SAMPLE IN EDUCATION RESEARCH SAMPLING VARIABLE DATA 2.…
-
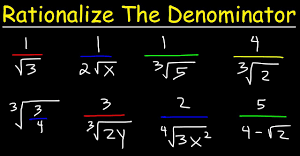
Rationalizing a denominator: concise easy approach2
Rationalizing a denominator means eliminating any radicals (like square roots) from the denominator of a fraction. To do this, multiply both the numerator and denominator by a value. This value should make the denominator a perfect square or a rational number. Here’s an example: Suppose you have the fraction: To rationalize the denominator, you multiply…
-
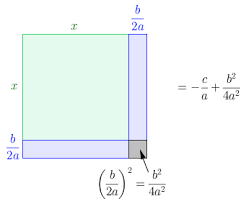
Quadratic expressions and equations: concise Introduction 1
Quadratic expressions are algebraic expressions of the form ax2+bx+c where a, b, and c are constants and a!=0. Constants means real numbers. if a=0, the expression would be linear rather than quadratic. When a graph of a quadratic expression is plotted against x ,is a parabola is formed. If a is greater than 0, the…
-
Form 4 schemes of work term 1 2025.
Here is form 4 schemes of work for term one. Related topics
-
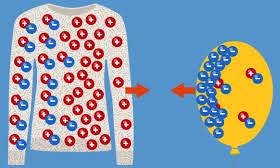
Charging bodies in electrostatics 1
In electrostatics, charging bodies means adding or removing electrons from atoms of objects. This results in an imbalance of electric charge. If electrons are added, the object becomes negatively charged; if electrons are removed, it becomes positively charged. This creates an electric field around the charged object, which can exert forces on other charged bodies.…
-
Consider a circle of radius r on a Cartesian plane centered at point o(a,b) as shown in figure below. A point p on the circumference of the circle has an arbitrary point (x, y). line OQ an QP makes a right angle triangle with the radius r of the circle such OP=r, OQ = x-a…
-
Alter lives
What is the greatest gift someone could give you? The gift of life one can give is something that can help one achieve their dreams. Because it is in the dreams we have everything else we need in life. Peace of mind, joy of the spirit and fulfilment. Remember that whatever one can get in…
