In electrostatics, charging bodies means adding or removing electrons from atoms of objects. This results in an imbalance of electric charge. If electrons are added, the object becomes negatively charged; if electrons are removed, it becomes positively charged. This creates an electric field around the charged object, which can exert forces on other charged bodies. The charge on an object is measured in coulombs (C). Charging can occur through methods like friction, conduction, or induction.
Charging by Induction
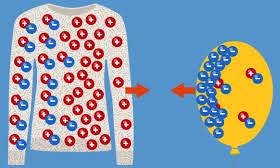
Charging by induction is a process where an electrically neutral object becomes charged without direct contact with a charged object. It is process of charging a neutral body without requiring direct contact between the objects. This method relies on the influence of the electric field to bodies.
When charging a body by induction, a charged object (either positive or negative) is brought near a neutral conductor. Electric field of the charged object causes the charges in the neutral object to rearrange in what is called polarization. Another word for polarization is separation of charges. Electrons in the neutral object respond to the external electric field. They either move toward or away from the charged object. This creates a region of excess negative charge near the charged object.
There is also a region of positive charge on the opposite side. If the neutral object is grounded (earthed), electrons will flow into the object when the nearby object has a positive charge. Electrons will flow out of the object when the nearby object has a negative charge. This step ensures a permanent charge on the object. After grounding, the external charged object is removed. The object now retains a net charge of the opposite type.

Leave a Reply