In summary
Language of thin lenses means that thin lenses have their own vocabulary mostly that describes various parts of the lens. This parts includes:
- Center of curvature C
- Radius of curvature R
- Principal axis P
- optical center O
- Principle Focus F
- Focal Length f
- Focal plane
We will discuss all the highlighted parts in this lesson
Center of Curvature C
It is defined as the center of the sphere of which the surface of the lens is part.
We consider the lens to have been cut off from a transparent sphere of radius R. In other word, the lens is part of a curved surface of a certain sphere as illustrated below.

For bi-convex lens, the lens is considered to come from two pieces cut from two different spheres and combined at the inner side. Consider the illustration below where we extract service1 and service2 from two spheres.


Because the bi-convex comes from two spheres, it will have two centers of curvature which will be opposite to each other.

similarly the bi-concave lens is derived from two spheres as illustrated.

Different parts from spheres will be joined two have a concave lens that has two centers of curvature as shown below

Radius of curvature
It can be defined as the radius of the sphere from which the surface of the lens is part.
It can also be defined as the distance between the Center of curvature and the optical center o of the lens.
Principal axis
It is an imaginary line passing through the centers of curvature and is perpendicular to the plane of the lens.

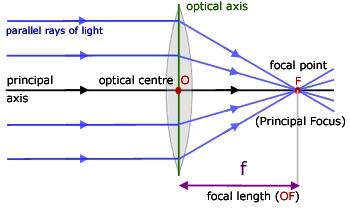
Optical center
It is the geometric center of the lenses where a ray incident to the lens passes on undeviated.
Principal focus
Sometimes also referred to as the focal point, It is a point on the principal axis where rays parallel and close to the principal axis converge after refraction by a convex lens or where the rays parallel and close to the principal axis seems to diverge from after refraction by a concave lens.
The figure below illustrates convergence of parallel rays of light at principal focus after refraction.

The virtual principal focus of a concave lens is as illustrated below

A lens has two principal foci, and they are on either side of the lens.
The principal focus of converging lens is said to be real because their actual meeting of rays of light there.
The principal axis of diverging lens is said to be virtual (imaginary) because rays of light do not actually meet there.
Rays that are parallel and close to the principal axis or almost parallel to the principal axis are referred to us paraxial rays.
Rays parallel but far from the principal axis are referred to as marginal rays or axial rays.
Focal length f
It is the distance between the optical center of the lens and it’s principal focus.
By Convection, focal length of converging lens is considered real while that of diverging is considered virtual.
Focal plane
It is an imaginary plane that passes through the focal point and is perpendicular to the principal axis.
Focal plane is illustrated below

rays of light that are not parallel to the principal axis converges at a point on a focal plane or will appear to diverge from there after refraction
Conclusion
In this lesson we have seen that lens are pictured as being extracted from a sphere and the radius of the said sphere plays and important role in description of the lens. A lens converge or diverges rays parallel to the principal axis at the focal point.

Leave a Reply