Questions on measurements on measurements are many. Here are some practice questions that will help you practice and understand the topic better.
In physics, measurements refer to determining the quantity of a physical property. This includes properties like length, time, mass, or temperature. These are measured using specific tools or instruments. Questions on measurements in physics typically cover:
- Units of Measurement: These define how quantities are expressed. The International System of Units (SI) is commonly used. It includes standard units like meters (m) for length. Kilograms (kg) are used for mass. Seconds (s) measure time.
- Precision and Accuracy:
- Accuracy refers to how close a measured value is to the true or accepted value.
- Precision refers to the consistency of measurements when repeated under the same conditions.
- Significant Figures: These show the precision of a measurement. The number of significant figures in a result reflects the certainty of the measurement. Trailing zeros in decimal numbers and non-zero digits are considered significant.
- Error and Uncertainty:
- Systematic errors are consistent and predictable, while random errors vary unpredictably.
- Uncertainty quantifies the doubt in a measurement, often expressed as a range (e.g., ±0.1).
- Conversion of Units: Understanding how to convert between different units of the same quantity is important. For example, converting kilometers to meters is essential for consistency in physics calculations.
These questions help assess the understanding of measurement principles, ensuring correct interpretation and analysis of physical quantities.
Basic Questions on Measurements
- Distinguish between basic and derived quantity. Give two examples in each case. (4marks)
2. Complete the table below. (7mks)
| Quantity | SI Units | Symbols of SI Units |
|---|---|---|
| Luminous Intensity | ||
| Ampere | ||
| K | ||
| Kilograms | ||
| s | ||
| Mole | ||
| Length |
3. Draw a burette filled with water to a volume of 28cm3. (2mks)
4. 60 drops fell from a burette. The first and final readings were 28cm3 and 42cm3 respectively. What is the average volume of one drop. (3mks)
5. Determine the density in SI Units of a solid of mass 40g with dimensions 30cm by 4cm by 3cm. (4mks
6. 1600cm3 of fresh water of density 1g/cm3 are mixed with1200cm3 of sea water of density 1.2g/cm3. Determine the density of the mixture. (4mks)
7. A sphere of diameter 6.0cm is molded into a thin uniform wire of diameter 0.2mm. Calculate the length of the wire in metres. ( Take π=22/7) (3mks)
8. Find the area of the shaded region in the figure 1 below (use π = 3 .14)(3mks)

9. A test-tube has a diameter of 3cm. how many turns would a piece of thread of length 90.42cm make round the test tube.(Take π=22/7) (3mks)
10. A cylindrical column of fat has diameter 17.5cm and height 10cm. Calculate the density in g/cm3 of fat if the column has a mass of 2kg. (3mks)
11. The following figure represents a piece of land . The two ends are semicircles of radius 70m each.

- Calculate
- The perimeter of the land (2mks)
- The area of the land in hectares (3mks)
12. The diagram below shows a piece of wood whose length is being measured using a strip of measuring tape.
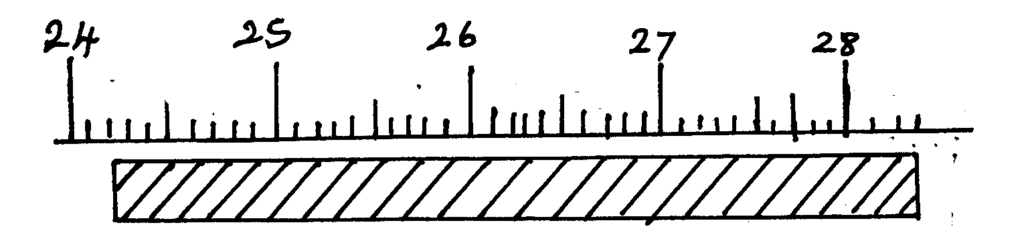
What is the length of the piece of wood.
13. Figure 1 below shows a Vernier calipers being used to measure the thickness of an object. It has a error of +0.01cm.
What is the correct measurement? (2mks)
14. Figure 1 below shows a burette that was initially filled to 90ml.
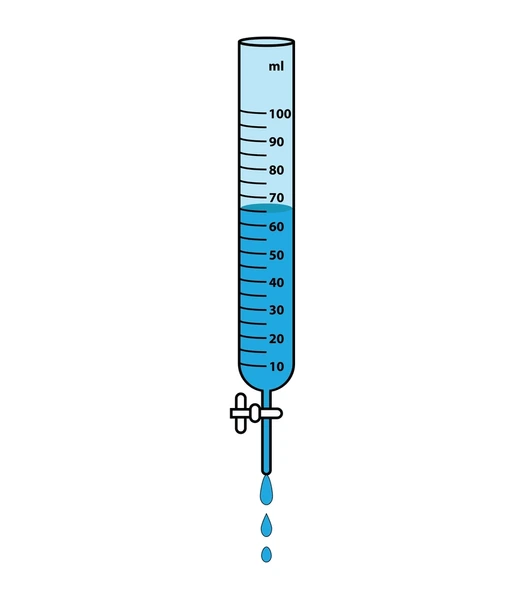
If the volume of liquid removed from the burette has a mass of 11g, determine the density in gcm-3. (Leave your answer in 2 decimal places) (2 marks)
15. Fig. 1 shows a cylinder filled with water and ten lead pellets each of volume 1.8cm3.
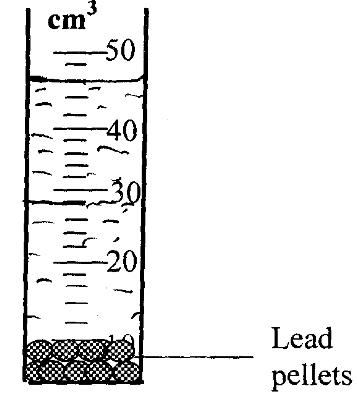
Indicate on the diagram the level if the pellets are removed. (1 mark)
16. In an oil drop experiment a student estimated the diameter of the oil patch to be 0.16m, given that the volume of the oil drop was 0.048cm3, calculate the thickness of the oil patch. (3mks)
17.The figure below shows Hare’s apparatus used for comparing liquid densities.
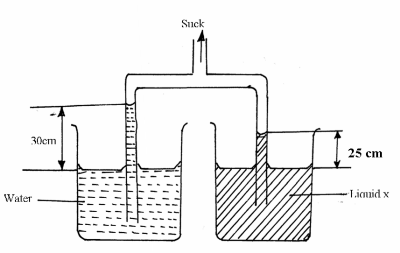
Use the information given in the above diagram. Calculate the density of liquid x. Note that the density of water is 1000kgm-3. (2mks)
18. Figure below shows part of a scale of a Vernier calipers.
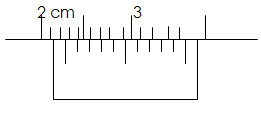
What is the reading indicted by the scale? (2marks)
19. The vernier caliper in the figure below has a zero error of -0.05cm
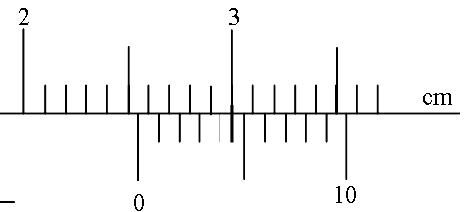
State the actual reading of the measuring instrument. (2mks)
20. The figure below shows a measuring cylinder containing some water.
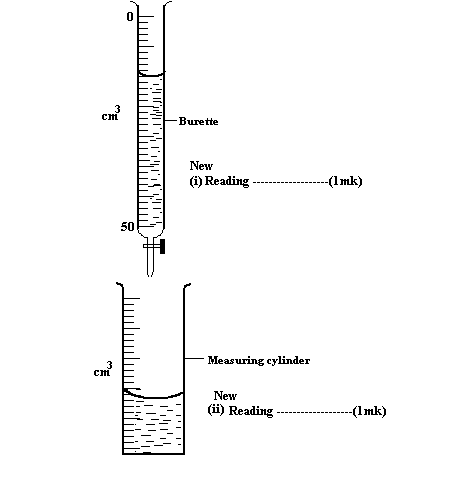
Another 10cm3of water was in to the cylinder from a burette delivering volumes from 0 cm3 to 50 cm 3. Record in the spaces provided the new reading indicated on each vessel. (3 marks)
21. Draw a section of a Vernier calipers showing a reading of 10.35cm. (2 marks
22. The figure below shows a micrometer screw gauge used to measure the diameter of a piece of wire
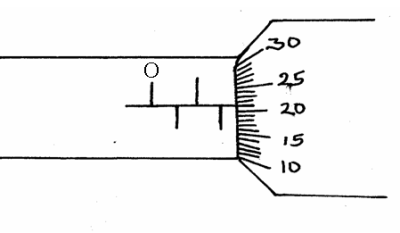
Figure 1
(i) Determine the reading on the scale of the micrometer screw gauge (1mark)
(ii) If the micrometer screw gauge has an error such that if the jaws are closed without any object, it reads 0.04mm below the center line of the sleeve, determine the actual cross – sectional area of the piece of wire (2mks)
22. What is the reading on the micrometer screw gauge shown below with an error of +0.5mm?
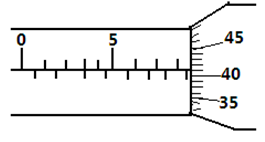
(1mk)
23. Ten glass marbles, each of mass 6.0 g, were gently lowered into a 100cm3 measuring cylinder containing water to the level marked A. The water level rose to the level marked B as shown in Fig. 1 below
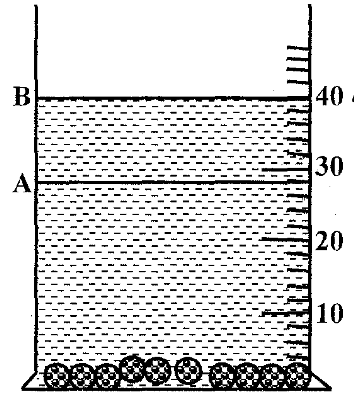
Determine the density of the glass. (3mks)
Related Topics
- Physical Quantities
- Length
- Reading a meter rule
- Measuring with a meter rule
- Area
- Area of irregularly shaped surfaces
- Volume
- Volume of regularly shaped objects
- Measuring volume of liquids
- Volume of irregular solids
- Measuring Mass
- Density
- Finding density: Concise Introduction 1
- Densities of some substances
- Questions on Measurements


Leave a Reply