Electric field patterns represent the direction and strength of the electric field created from charged objects. The electric field is a vector field. It shows the force exerted on a positive test charge at any point in space. Electric field patterns show how charged objects interact. They also illustrate how these charges influence the space around them.
Some properties of electric fields
Electric fields have unique properties that dictates their behavior in a microscopic levels. This properties includes:
Direction property
The direction of an electric field is usually described as the direction a positive charge would move if placed inside a positively charged field. According to the basic law of charges, there are only two types of charges. This charges are positive and negative charges. Positive charge will move away from a positive charge and negative charge will move towards a positive charge.
The electric field points away from positive charges and towards negative charges.
Electric field Strength
The field is stronger closer to the charge and weaker as you move farther away. The strength of the electric field is thus proportional to the charge and inversely proportional to the square of the distance from the charge. We will discuss this in details later on.
Electric field Field lines
Electric fields are represented by imaginary lines often referred to as Electric field Field lines. These lines show the direction of the field and also the strength in the field. They are denser when there field is strong fields and scarcely populated when fields are weak .
For a positive charge, lines radiate outward. For a negative charge, lines converge inward as we are going to see soon.
Electric fields are parallel
Electric fields runs parallel to each other and never cross.
In parallel plate capacitors or between two oppositely charged plates, the electric field is uniform, with parallel, equally spaced field lines.
Superposition: The total electric field due to multiple charges is the vector sum of the fields from each individual charge.
We shows some common electric field patterns due to charged particles:
Electric field pattern for a positive point charge
A positive charge has it’s electric field radiating outwards from the center as shown. The lines are radial moving away from the point charge and never meets. They are parallel and uniform.
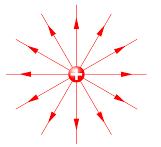
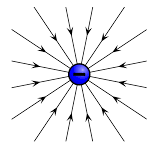
Electric field pattern for a negative point charge
A negative point charge will have it’s electric field radiating inwards from infinity towards the center of the point charge. Just like in positive charge, the field lines are radial and parallel as shown.
Electric field pattern between two positive charges
The electric field patterns for two positive charges will resemble how they behave in an individual positive charge. They move radially from the center. However, they bulge away as they come closer. Due to repulsion, the two field lines can never meet. They curve to avoid each other at the point of approach. see the figure below.
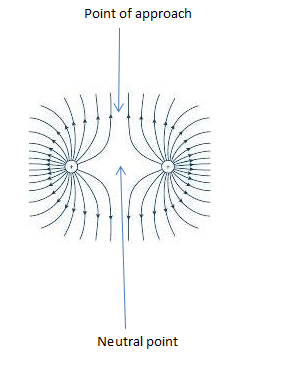
The neutral point is a point where effects of the field cannot be felt. This is because the two opposing electric fields cancel each other’s effect.
Electric field pattern between positive and negative charge
A negative charge will always be attracted towards the positive charge. The electric field pattern when a positive a negative charge are close to each other is that of radial lines running from positive towards the negative charge. the lines are parallel and uniform. see the figure below.
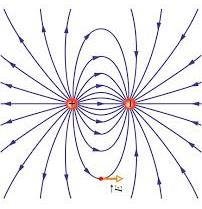
As you can see on the diagram above, the direction of the field line is from positive point charge towards the negative point charge.
Electric field pattern between two negative charges
The pattern is similar to the one between positive charges except that the fields direction are towards the point charge. At the approach point, the field lines bulge as the try to move away from each other. If the charges are brought too close to each other, the repulsion force increases. This force causes the two point opposing charges to move away from each other. see the diagram below.
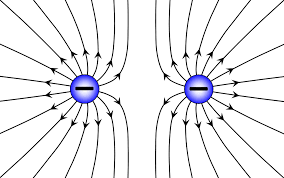
The closer to the charge you go, the denser the lines become, indicating a stronger electric field near the charge. As you move farther away, the lines spread out, showing that the field weakens with distance.
For a point negative charge, the electric field lines radiate inward toward the charge. Their strength decreases with distance from the charge.


Leave a Reply