Category: Science People
-
Integrating products of trigonometric functions 1
Products of trigonometric functions usually refers to the integral of a product of trigonometric functions over a specified range. It can be interpreted as finding area under the curve made by a trigonometric function. For example the function: represents area under the curve formed by the product of sine and cosine functions. The integral results…
-
Center of Gravity:1 Definition and Applications
The center of gravity (CG) of an object is the point where its entire weight can be considered to act. It is the average location of the weight distribution of an object. In simple terms, it’s the balance point of the object. Explaining Center of gravity An object is considered to be made up very…
-
What Variance? 1 easy Simple Guide
Variance is a measure of the spread or dispersion of a set of data points in a dataset. It quantifies how much individual values differ from the mean (average) of the data.
-
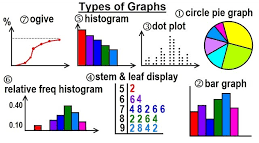
8 useful Statistical graphs
Statistical graphs are visual representations of data that help to understand and interpret trends, patterns, and relationships. Here are some common types of statistical graphs: 1. Bar Graph (or Bar Chart) Description: A bar graph uses rectangular bars to represent the frequency or value of categories of data.Use: It is used to compare different categories…
-
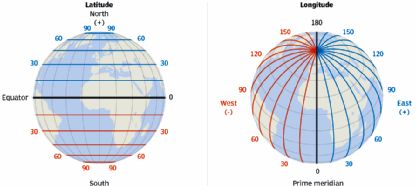
Longitudes and latitudes : A concise Introduction
Longitudes and latitudes are imaginary lines used to locate positions on the Earth’s surface. Latitude and longitude are lines used to locate locations on planet earth. Longitudes as from the Greenwich Meridian It is a historic prime meridian or the Greenwich meridian used as a geographical reference line that passes through the Royal Observatory, Greenwich,…
-

Data capacity: A Free Concise guide1
Data Capacity of CDs Data capacity for a given storage device is the size of data such a device can be able to hold. You can fit on a S/VCD without over burning: You can fit on a CD-ROM without overburning: Introduction Let us ignore for now the terms of megabyte for CD capacity and…
-
Linear Magnification
Linear magnification refers to the ratio of the size of an image to the size of the object that produces it, when viewed through an optical instrument like a microscope, telescope, or camera. In simpler terms, it’s how much larger or smaller the image appears compared to the actual object. For example, if a microscope…
-

Albert Einstein: Theory of relativity
Albert Einstein was a Jew born by Jews Parents living German Empire in 19th century And became a theoretical physicist who is considered one of the greatest and most influential scientists of all time.
-

Isaac Newton: One Great scientist of all times
Sir Isaac Newton was an English scientist active as a mathematician, physicist, astronomer, alchemist, theologian, and author who was described in his time as a natural philosopher.