Domestic wiring refers to electrical connections and setups done in order to allow use of electric powers supplied by electric power providers to the consumers.
Electrical power is usually supplied at 240V after the high voltage transmitted is scaled down through a local transformer. The high voltage transmission from power source could be 11000v or more. The consumer will need only 240v, therefore a stepdown transformer will be needed.
Electric power is connected to a homestead from the transformer by use of two-wire cable, one of which is earthed at the transformer.
The earthed wire is referred to as the neutral wire .
The earthed considered to be at zero electrical potential while the other wire is referred to as the live wire.
The cable goes through the electrical company fuse box where the live wire is connected to a 60A or hire fuse value. The cable is then connected to the power meter where energy consumption is registered and from there it passes on to the consumer’s fuse box as illustrated.
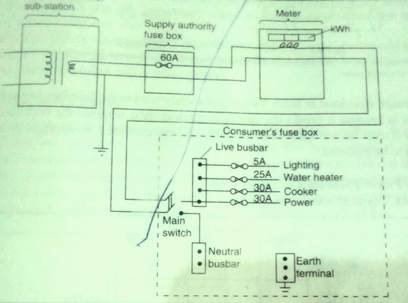
The consumer fuse box in domestic wiring will have main features as in the diagram above which we describe in the figure below.
The main switch
This is a double -pole switch which disconnects both the live and the neutral wire at the same time. disabling all the circuits in the house when needed. It is the main connecting link between external supply and household wiring but we can have more than one mains switch.
The live busbar
This is a brass bar to which all live wires and the fuse are connected to. It connects to the live wire through the main switch and connects the live wire of each circuit through a fuse.
Neutral busbar
This is the brass bar to which all neutral wires are connected to in domestic wiring.
Earth terminal
It is the earthed cable in the fuse box connected to the thick copper bar burried deep in the earth. It can also be earthed through water piping.
fuses
They are made of short thin wire mostly an alloy of cooper and tin. The alloy wire should have a low melting point. Fuses are used to safeguard against excess current in the circuit. When current exceeds the fuse rating, the wire gets very hot and melts hence disconnecting the circuit.
The melting disconnects the excess current which would have otherwise damaged the electrical appliances. Fuses also reduces risk of fire incase there is overheating in a circuit.

The circuit breaker
Circuit breakers are preferred over fuses protect electrical components from excessive flow for current.
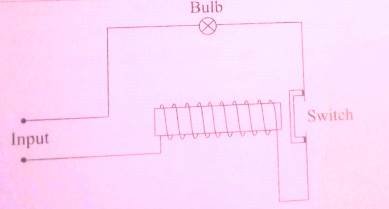
When excess current flows through the circuit, increased magnetic power of the electromagnet opens the switch , stopping electric current flow. Once the problem causing the excessive current flow has been corrected , the switch is closed by mechanical means.
One advantage of circuit breaker over the fuses in domestic wiring is that the circuit is broken simultaneously where the fuse melts slowly. The circuit breaker reset itself once the electric surge is corrected as opposed to fuse that need to be replaced when it’s fuse wire melts.

Leave a Reply