Electrostatics is a branch of physics that deals with behavior and properties of charges that are not flowing. When materials are subjected to mechanical friction force against other materials, the electrons near the surface jump out from one material and become logded to the other material. In other word, when materials rub each other, electrons are transferred. The transfer of electrons is what is referred as charging of the material.
Materials are made from matter and matter is made of atoms. Atoms are considered to be very tiny particles whose size is in the order of 0.1 nanometers and that cannot be divided further. Atom is considered as the blue print of every matter whether it is a gas, liquid or solid. They are the basic structures that are joined together to make molecules that composes matter.
Structure of an atom
Atom is made up of two parts, a central core called nucleus and outer orbits where electrons goes around the nucleus. The nucleus contains particles called protons and neutrons closely and tightly packed inside.
Protons carries a positive charge whereas electrons carries negative charges. Neutrons carries no charge.
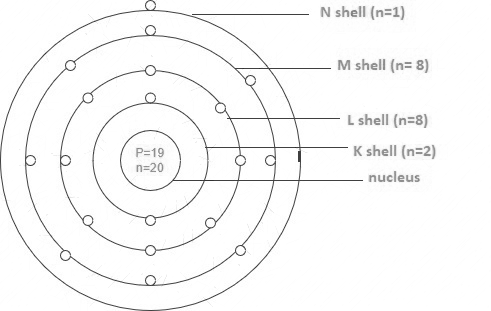
The number of protons and electrons in an atom are equal in number such that the resultant charge is zero. This is because there are equal number of positive charge as there are negative charge so that they cancel out each other making the overall charge in an atom to be zero.
Causes of electrostatics charging
In some materials , electrons are not tightly bund to the nucleus and so when given some little energy, they tend to jump out of the atom. When two materials are rubbed against each other, the heat energy developed due to friction may cause some loosely held electrons from one material to move and be transferred to the other material. Some materials easily losses elecrons whereas others readily accepts electrons during friction.
Materials that losses electrons are said to be positively charged because they have overall more positively charged protons compared to electrons.
Materials that gains electrons are said to be negatively charged because they have overall more negatively charged electrons as compared to the protons. As an example, when polythene is rubbed against flannel clothe, it gains electrons and becomes negatively charged . Consequently, flannel clothe becomes positively charged because it looses some of its negatively charged electrons to polythene.
Glass will loose electrons to silk when they are rubbed together making the glass to gain positive charge and silk to be negatively charged.
The following has been observed when materials have been charged by friction.
- Excess negative charge on one body is equal to excess of positive charge on the other body and so no new charges is ever created. charges are never created, they are only transferred.
- Some materials will always acquire they same type of charge during charging and so it may be possible to predict the charges on materials after you rub them together.
- The quantity of charge in some cases maybe small and in some cases charges may escape before they are detected. When charging by friction, the idea environment is a dry atmosphere and clean charging bodies to avoid discharge.
Some Experiments to explain electrostatic charges
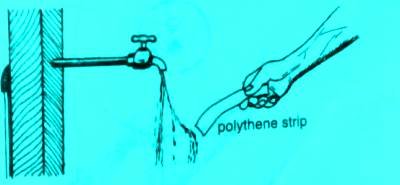
Take a polythene strip and rub it against silk and then take the strip near a thin stream of flowing tap water as shown:
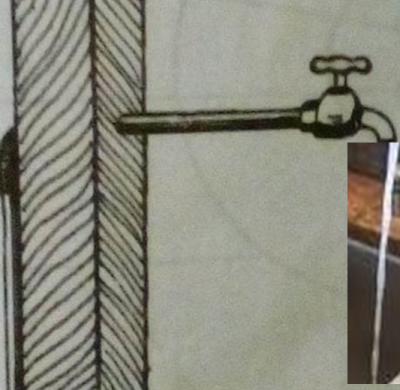
When a charged strip is brought near a thin stream of water, the of water is strongly attracted to the polythene as shown.
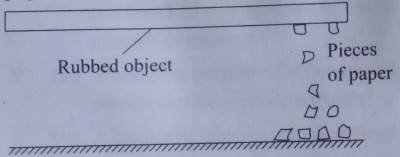
when a plastic comb, pen or plastic ruler is rubbed against your clothe or hair, it is observed to attract small pieces of paper as shown.
A household mirrors and windows attract dust and other particles when wiped with a dry clothe because of electrostatic charges.
All the above observations are as a result of electrostatic charges.
There are two types of charges namely negative and positive charges. The SI unit of charge is the coulomb(c).
- 1 Coulomb = 1000 millicoulombs
- 1 millicoulomb = 1000 microcoulombs
- 1 coulomb = 1000 000 microcoulombs

Leave a Reply