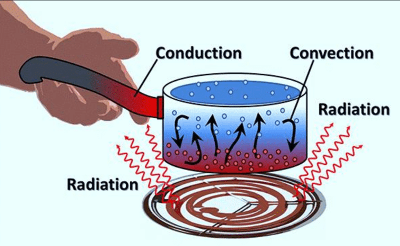
Heat conduction is a process by which heat moves in solids by means of vibrations of it’s molecules.
If you put one end of iron on fire, soon the other end will be hot, sometimes too hot to handle. The heat energy entering the iron from the hot end increases the vibrations of atoms. Atoms in that end then collides with their neighboring atoms, increasing vibrations of the neighbor atoms, passing the heat energy along.
Metals have free electrons which travels throughout the body freely and randomly. Heat energy injected at the hot end of a metal increases vibrations of the particles at that end causing the free electrons in that region to gain more kinetic energy and because they are moving freely, they carry energy to other parts of the metal making heat conduction in metal faster than in other forms of matter.
Different solids conducts heat differently, where some solids like aluminum conducts heats very fast whereas rate of heat transfer in wood and rubber is extremely slow, almost zero.
to compare heat conduction of various materials, consider an experiment with the following materials:
- Rods of aluminum
- iron
- rubber
- glass
- wood
- source of heat
- thermal conductivity tank
The materials listed should be of the same length and thickness.
procedure to investigate heat conduction
- setup the apparatus as shown ensuring that the rods are firmly held before poring boiling water into the water bath.

- observe the order in which solid fat fixed at the end of the materials melts and fall.
observations
The wax on end of copper rod melts before any other, then it was followed with the one on aluminum and the one on iron was third.
This shows that copper conducts heat faster compared to aluminum and aluminum conducts heat faster compared to iron.
wax on glass will melt after sometimes but the one on wood and rubber will not melt. In fact the boiling water will cold before they melt.
Explanations of heat conduction
Different materials have different thermal conductivity. Metals being good conductors of heat and non metals being poor conductors of heat.
solids that are poor conductors of heat only conducts heat by vibrations of atoms which can be slow. They don’t have free electrons to move heat faster.
poor conductors of heat are very useful because they are used as insulators where we need to prevent heat flow.
Good conductors of heat are also very useful in making of cooking pots and heat sinks.
Sometimes we need good conductors of heat and other times we need poor conductors when heat movement is not desirable. So both poor and good conductors are important to us. None is more important than the other.
some of the good conductors of heat in decreasing rate of conduction includes:
- silver
- copper
- aluminium
- brass
- zinc
- iron
- lead
- mercury
some of the poor conductors of heat in decreasing rate of conduction includes:
- concrete
- glass
- brick
- asbestos paper
- rubber
- wood
- water
- air

Leave a Reply