In physics, Measuring volume is a measuring of the three-dimensional space occupied by a substance or enclosed within a container. It is typically measured in cubic units such as cubic meters (m³) or cubic centimeters (cm³).
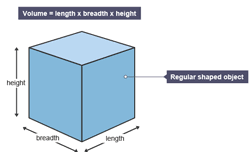
Volume as a three dimensional quantity, is obtained when three lengths are multiplied together.
Another popular definition is that volume is a measure of space.
because volume results from product of three lengths, the SI unit of volume is cubic-meter(m3). That is, SI unit of volume is the cube of the SI unit of length. This tells us that volume is a derived quantity.
However, There are common sub-multiples of volumes like:
- cubic-centimeters (cm3)
- cubic-millimeters (mm3)
- cubic-micrometers (µm3) ………….just to name a few.
1m3 =1m x 1m x1m
but 1m =100cm
hence 1m3 =100cm x 100cm x 100cm = 1000000cm3.
From Volume, we can find units of capacity like litres(l) and millitres(ml).
1 ml =1cm3
1 litre = 1000ml
1 m3 = 1000 litres.
when you buy a half litre packet of milk from the supermarket, you are actually buying 500ml of milk.
Example in Measuring Volume: Converting mm3 to m3
Express 43.5mm3 into m3.
Solution

Example
convert 0.00006 m3 into cm3
Solution

practice Questions
The radius of a typical atom is considered to have a volume of 10-10m3. Express the given volume in:
- mm3
- cm3
- µm3
Related posts
- Length
- Physical Quantities
- Reading a meter rule
- Measuring with a meter rule
- Area
- Area of irregularly shaped surfaces
- Volume
- Volume of regularly shaped objects
- Measuring volume of liquids
- Volume of irregular solids
- Measuring Mass
- Density
- Easy Integration: partial fractions
- Densities of some substances
- Questions on Measurements

Leave a Reply