Volume of irregular solids are measured using a method known as displacement. A solid whose volume is needed must NOT be soluble in water. The method involves immersing the object in water. Similarly, the object should NOT be capable of absorbing water nor reacting with water.
Displace methods can be used in two different ways to measure Volume of irregular solids:
- Using Measuring cylinder
- Using a Eureka can
Volume of irregular solids using a measuring cylinder
The basic principle behind this method resembles Archimede’s principle. The volume of water displaced by the solid in the measuring cylinder shows the actual volume of the solid.
Some water is placed in a measuring cylinder. We call its volume V1. This volume is then read and recorded as shown in the diagram below.

After the volume is read, the solid is tied on a string and slowly lowered into the measuring cylinder. The new Volume V2 of the liquid is recorded as in figure below.

The change in volume from V1 to V2 represents the addition of volume added by the solid as per the Archimede’s principle; hence the volume of the solid will be given by
Vs = V2-V1 where Vs = volume of the stone
Volume of irregular solids using a Eureka can
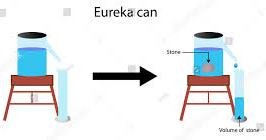
A Eureka can (also known as a displacement can) is a container with a spout from the side. Any liquid that is beyond the spout level flows out through the spout. It is also known as an overflow can.
Our stone stands for any solid whose volume can be measured. It displaces the water. This displacement causes the water to flow through the spout.
Consider the diagram below.

Before the stone is immersed, you make sure that the water is at the level of the spout exactly. It is an important step because it determines accuracy of your measurements.
You ensure the level is correct by adding some water to the can. Then, wait until it stops overflowing. You then bring a dry and clean measuring cylinder under the spout before lowering the stone as shown here.

After the stone is lowered into the can, the water it displaces flows out of the spout.
The volume read from the collected water in the measuring cylinder is the volume of the stone.
Experiment to determine Volume of an objects that floats on water surface
The idea behind the exercise is to tie a floating object onto the object that sinks into water so that both can sink. It is like increasing the density of the floating object so that it exceeds that of water.
Apparatus:
- Eureka can
- measuring cylinder
- plastic cork
- small metal block(sinker)
Procedure:
- Fill the Eureka can with water such that you allows excess water to flow through the spout as in figure below.

- After water has stopped flowing through the spout, place a measuring cylinder under the spout.
- Tie the sinker with a thread and lower it gently into the can as in figure below.

- Measure the volume V1 of the water that overflows and is collected into the measuring cylinder.
- Remove the sinker and tie it to the cork as shown

- Fill the Eureka can again and allow excess water to flow out
- When water stops flowing from the spout, place a dry clean measuring cylinder under the spout.
- Lower the sinker and the cork tied together gently into the eureka can as illustrated below.

- Measure the new volume V2 that is collected into the measuring cylinder.
The water collected in the measuring cylinder is the volume of the sinker and cork combined. If we subtract the volume V1 collected earlier for the sinker alone, we finds the volume of the cork.
Therefore, Volume of the cork Vc = V2-V1
Conclusion
In this lesson, we discussed about finding volume of irregular solids. The method we discussed is called displacement method and it involves immersed the object in water and determining amount of water that is displaced by the object.
related Lessons:
- Units of measuring volumes
- Volume of regular solids
- Measuring Volume
- Measuring Volume of liquids
- Area
- Length

Leave a Reply